Mr. Sanchez was transferred to the medical unit mid-morning. The team is preparing for his discharge in 1-2 days.
A team-based approach in HF management has been shown to:

Please click on each of the buttons below to learn what each provider is responsible for at this time.
Albert, N. M., Barnason, S., Deswal, A., Hernandez, A., Kociol, R., et al. (2015). Transitions of care in heart failure: A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation Heart Failure, 8, 384-409. doi: 10.1161/HHF. 0000000000000006
It is also important to involve a family member or friend designated by the patient as part of the care team.
As the inpatient provider, what are some of the methods to provide proper handoff to Mr. Sanchez’ primary care provider (PCP) about the events of his recent hospitalization?
Please drag the bottom right corner to expand the box.


If the discussion of goals of care with Mr. Sanchez’ indicated an interest of moving towards optimizing quality of life versus continuing curative approaches, it would be appropriate to consult palliative care prior to discharge.
One week later, Mr. Sanchez visits his primary care provider. He arrives at the clinic accompanied by his wife. He is called back by the medical assistant (MA) and escorted to a clinic exam room. The MA asks Mr. Sanchez to have a seat on the exam table. She takes his vital signs and inquires about any complaints of pain. Mr. Sanchez denies complaints of pain, but tells the MA that he has felt tired since he has been at home.
The MA notifies the PCP that Mr. Sanchez is ready and waiting to be seen. The PCP logs into the EMR system and notes the following:
VS: T 37.0o C, HR 56 bpm, BP 101/62 mmHg, RR 16 bpm, SpO2 97% on room air (RA), weight 119.5 kg
Please drag the bottom right corner to expand the box.

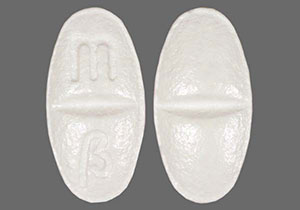
At this post-discharge follow-up visit, it is noted during medication reconciliation that Mr. Sanchez has not been taking his Metoprolol XL 12.5mg as ordered. He stated that he didn’t pick up his prescription yet, since he already had metoprolol succinate 25 mg in his medicine cabinet, so he decided to just take that for now until he runs out of it.
Please drag the bottom right corner to expand the box.
The PCP should explore why the patient chose to use up other medication first versus getting the new prescription filled. The PCP should also reinforce with Mr. Sanchez the importance of taking medications as prescribed and needs to explain that the prior prescription was actually a larger dose than the prescription he was sent home from the hospital with on discharge. The PCP should explain that his heart rate is a little slow and that might be the cause of him feeling tired, as well as fatigue can be a side effect of the medication. The PCP should use teach back methods to ensure Mr. Sanchez understands his medication regimen, and the rationale for the lower dose.

Mr. Sanchez’ PCP changes his medication regimen to include metoprolol XL 12.5 mg orally daily and discontinuing/discarding the metoprolol succinate supply remaining at the patient’s home.
The PCP arranges for Mr. Sanchez and his wife to visit the outpatient clinical pharmacist in the clinic after his PCP visit as part of the multidisciplinary approach to managing heart failure.
Please drag the bottom right corner to expand the box.
McNeely EB. Treatment Considerations and the role of the clinical pharmacist throughout transitions of care for patients with acute heart failure. J Pharm Pract. 2016 Apr 28. pii: 0897190016645435.
Warden BA, Freels JP, Furuno JP, Mackay J. Pharmacy-managed program for providing education and discharge instructions for patients with heart failure. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2014 Jan 15;71(2):134-9. doi: 10.2146/ajhp130103.

Mr. Sanchez is seen back in clinic with his primary care provider one month later. He is taking medications as ordered, and though he doesn’t like the dietary restrictions, he states that “my wife is keeping me straight.” His weight has been stable within 1.5 lbs. and he reports no increase in symptoms. He notes that he has an appointment with the cardiologist in 2 weeks. He has returned to work, and has resumed his normal exercise regimen of walking. Mr. Sanchez and his wife walk approximately 3 miles most days of the week. He is excited about an upcoming fishing trip with his son in the next month. He recognizes the importance of living a healthy lifestyle to enable him to fully participate in and enjoy such a trip, and the impact heart failure exacerbations can have on his life.

You have now completed the case study.
Please click on the link below to provide feedback on your experience.

Please listen to the conversation and suggest how improve it.
Please listen to the conversation below and suggest how improve it.
Please drag the bottom right corner to expand the box.
Please drag the bottom right corner to expand the box.
McNeely, E. B. (2016). Treatment considerations and the role of the clinical pharmacist throughout transitions of care for patients with acute heart failure. Journal of Pharmacy Practice. doi: 10.1177/0897190016645435
Tingley, J., Dolansky, M. A., & Walsh, M. N. (2015). Team-based transitions of care in heart failure. Heart Failure Clinics, 11(3), 371-378. doi: 10.1016/j.hfc.2015.03.003.
What is the role of the acute care provider/hospitalist while caring for patients on the medical surgical unit during the transition from inpatient to outpatient care?

What is the role of the clinical pharmacist in the care of patients with HF prior to discharge?

McNeely EB. Treatment Considerations and the role of the clinical pharmacist throughout transitions of care for patients with acute heart failure. J Pharm Pract. 2016 Apr 28. pii: 0897190016645435.
Wiggins BS, Rodgers JE, DiDomenico RJ, Cook AM, Page RL 2nd. Discharge
counseling for patients with heart failure or myocardial infarction: A best
practices model developed by members of the American College of Clinical
Pharmacy's Cardiology Practice and Research Network based on the Hospital to Home (H2H) Initiative. Pharmacotherapy. 2013 May;33(5):558-80. doi: 10.1002/phar.1231.
What is the role of clinical social worker in discharge planning for patients with HF?

Rasmusson, K., Benuzillo, J., Budge, D., Horne, B., Roberts, C. et al. High risk heart failure patient multidisciplinary care pathway: Improving care and outcomes. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 2015; 65(10), A1019.
What is the role of the dietician in planning for discharge of patients with heart failure?

Jaarsma T. Health care professionals in a heart failure team. Eur J Heart Fail. 2005 Mar 16;7(3):343-9.
What is the role of the nurse specializing in heart failure during transitions of care?

Self-management is when the patient participates in the care of his/her heart failure and involves healthy lifestyle modification, medication and other heart failure therapy adherence, understanding and recognizing signs and symptoms of worsening heart failure.
What is the role of the PCP during the transition of patients to outpatient care?
Manages care for an acute illness or injury, typically for a short duration while in a hospital setting. Depending on the setting, this may be a Physician, a Nurse Practitioner, or a Physician Assistant. Additionally, the acute care provider discusses and negotiates the plan of care with the patient and family.
Blood Alcohol Level: 0
INR: 1.0 (normal)
PTT: 35 seconds
CBC:
Hgb 9.9 g/dL
Hct 38%
Platelets 152,000/mm3
WBC 12,000 cells/mcL
Neutrophils 70% - Hi
Lymphocytes 23%
Monocytes 6%
Eosinophils 1%
Basophils 0.2%
BMP:
BUN 27 mg/dL
CO2 22 mmol/L
Creatinine 0.95 mg/dL
BUN/Creatinine Ratio: 28 - Hi
Glucose 310 mg/dL - Hi
Sodium 112 mEq/L - Lo
Chloride 85 mEq/L
Potassium 4.3 mmol/L
GFR calculated: 57.7 mL/min/1.73 m2 - Lo
Troponin: 0.01 ng/mL negative
CK: 50 U/L
U/A- wnl, except for + protein
Urine Toxicology Screen-negative
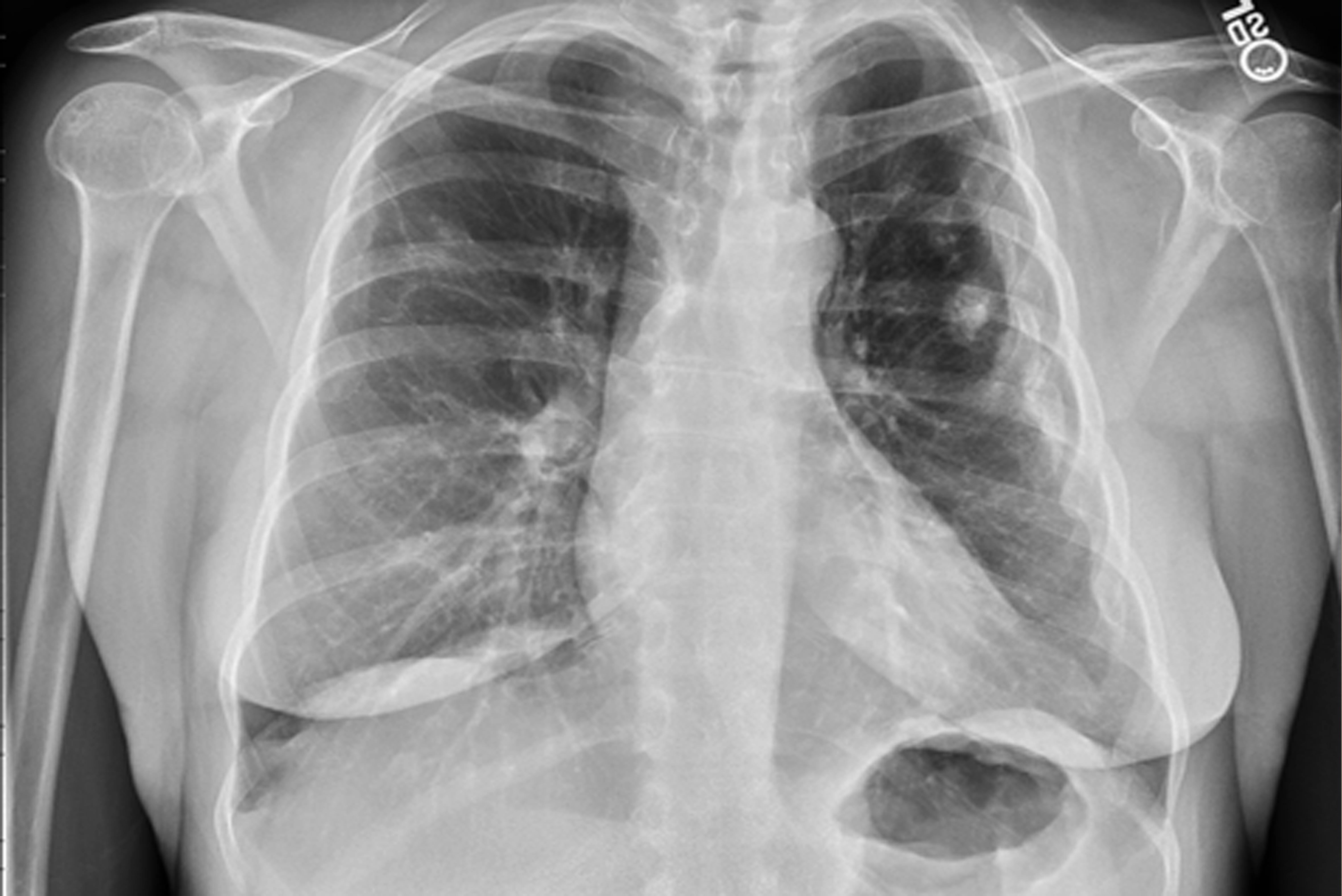
Multiple left-sided rib fractures. Most of these appear to be chronic and healed; however, there are acute-subacute appearing fractures of the anterolateral aspect of the left 4th and 5th ribs. Ununited chronic fracture of the lateral aspect of the left 6th rib.
Spine CT: No fractures.
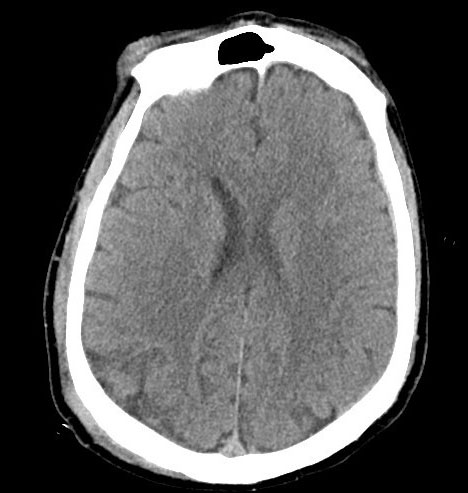
Head CT: 3mm right acute on chronic holohemispheric subdural hematoma without shift. No noted skull fractures.
Photo courtesy of UW Medicine.
The rationale for obtaining this consult is the presence of multiple rib fractures; need for assessment of possible elder abuse and locating legal next of kin (LNOK).
Social worker reports that she has attempted to contact patient’s daughter, but has not been able to reach her. Social worker will continue to reach out to daughter and locate other family members. Once family has been reached, social worker will conduct safety assessment for Mrs. Castillo, including assessing for possible elder abuse or neglect due to rib fractures.
The rationale for obtaining this consult is for surgical evaluation of the patient’s subdural hematoma.
Neurosurgery finds that the SDH is non-operable and recommends the transfusion of a 6-pack of platelets.

Aspirin therapy, such as Mrs. Castillo was receiving, disrupts platelet function by inhibiting COX-1 for the life of the platelet (~7-10 days). Presently, platelet transfusion for patients receiving antiplatelet agents, such as aspirin, is controversial and requires further study. A summary of work in this area is provided in the link below.